Leave Your Message
The use of Deep Sea Voltage Regulators is critical in today’s marine and industrial environments. According to a recent report by MarineTech Analytics, the global market for voltage regulators is expected to grow significantly, driven by advancements in deep-sea technology. Experts estimate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% from 2023 to 2028.
Dr. Jane Thompson, an expert in marine engineering, states, “Voltage stability is essential for underwater operations.” This highlights the importance of choosing the right Deep Sea Voltage Regulator. These devices provide essential power stability, preventing equipment damage from voltage fluctuations. Yet, many users often overlook the intricacies involved in selecting the right model.
Selecting the ideal regulator can be a complex task. Numerous factors come into play, including environmental conditions and power demand. Many customers struggle with the right specifications. Flaws or oversights can lead to operational issues. Understanding key features is vital. With proper knowledge, users can avoid costly mistakes in deep-sea projects.

Deep sea voltage regulators play a crucial role in various applications, especially in maritime environments. These devices ensure that electrical systems receive a stable voltage, which is vital for equipment reliability. An unstable voltage can lead to malfunctions or even damage to sensitive electronics. Understanding their function helps users appreciate their importance.
When exploring deep sea voltage regulators, considerations like the voltage range, load capacity, and environmental resistance are key. They often face harsh conditions, such as saltwater exposure and high pressures. Therefore, selecting a regulator with robust housing is essential. Many users overlook this aspect. They might choose based solely on price rather than durability, which could lead to failures.
The technology behind these regulators continues to evolve. Enhanced features, like digital monitoring, are becoming more common. However, not every regulator offers these innovations. Users should not just settle for the first option they find. Researching and considering operational needs is critical. This approach often reveals other factors that influence performance in deep-sea conditions.
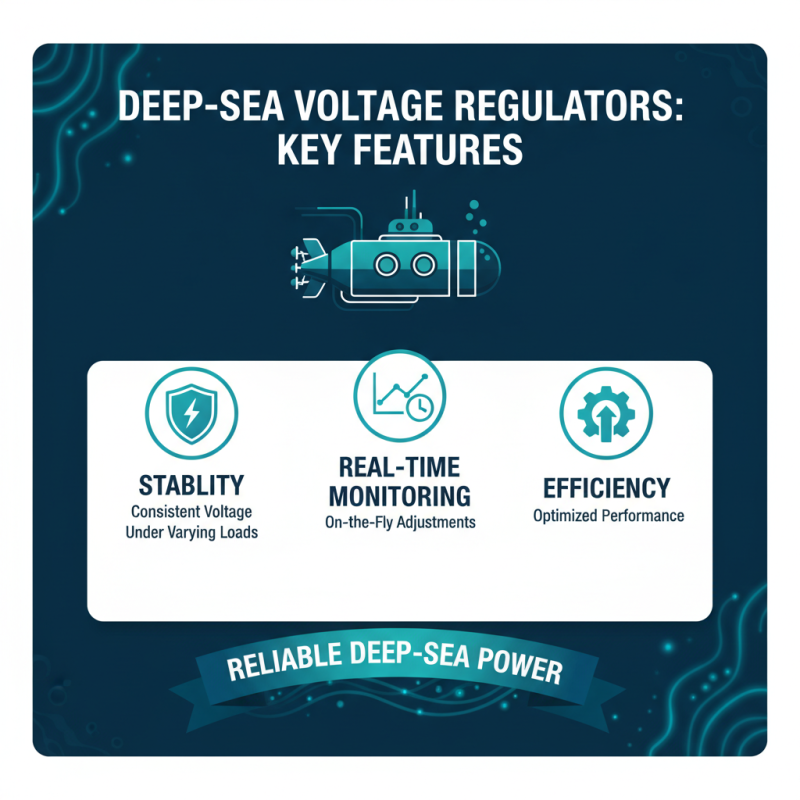
When considering deep sea voltage regulators, key features are essential. Stability is vital for reliable performance. Regulators should maintain consistent voltage levels, even under varying load conditions. Look for models that offer real-time monitoring. This feature allows adjustments to be made on the fly, enhancing efficiency.
Another crucial aspect is durability. Deep sea environments can be harsh. Regulators must withstand extreme temperatures and pressure. Corrosion-resistant materials are a plus. Power management features are also important. They help optimize energy usage, prolonging the life of both the regulator and the connected equipment.
Consider ease of installation and user interface. A complicated setup can lead to frustration. Intuitive controls make it easier to operate. While many features are beneficial, it’s essential to balance complexity and usability. Too many options can overwhelm users. Reflect on what is truly necessary for your specific needs.
When it comes to deep sea voltage regulators, knowing the right choice is vital. These devices help stabilize voltage in underwater operations. A proper voltage regulator can prevent costly equipment damage. Consider factors like depth rating, voltage range, and power output. Each regulator has unique features that serve specific needs.
A comparison of top models reveals various pros and cons. Some regulators excel in performance but may lack in durability. Others focus on efficiency but can be complicated to install. The trade-offs may not be clear at first glance. Understanding these aspects can guide better decisions.
Look for features like surge protection and temperature stability. These elements can significantly affect performance. Not all models perform equally in varying depths. So, testing is crucial. In the end, choosing the right voltage regulator is a balance between needs and limitations. It's a learning process that may involve some trial and error.
When installing a deep sea voltage regulator, several key steps ensure optimal performance. Make sure to choose a suitable location that remains dry and cool.
This helps prevent overheating and moisture damage. Before installation, always read the user manual for compatibility guidance. It provides essential information on wiring and safety protocols.
During installation, double-check all connections. Loose wires can lead to voltage fluctuations. It is wise to use quality materials to ensure lasting durability. Once installed, monitor the regulator for any unusual sounds or fluctuations. These could indicate potential issues that require immediate attention.
Maintenance is equally crucial for longevity. Schedule regular inspections and clean the unit. Dust and debris can accumulate, affecting efficiency. Replace worn-out components promptly. Keeping a log of maintenance activities can help track performance over time. Sometimes, noticing the smallest changes can prevent costly repairs. Adapting habits based on observations is key in this process.
Deep sea voltage regulators are essential in various industries. They ensure stable voltage levels in challenging marine environments. These devices protect sensitive equipment from voltage spikes and fluctuations. Many industries rely on them for consistent performance.
In marine applications, voltage regulators stabilize power for fishery vessels. They prevent damage to sonar and navigation systems. In offshore platforms, these regulators maintain voltage in extreme conditions. This reliability is critical for safety and efficiency.
Researchers constantly seek to improve these devices. Issues like corrosion and signal interference need attention. Addressing these challenges can lead to better performance. Many installations face difficulties, highlighting the importance of ongoing adjustments and evaluations.
| Model | Input Voltage (V) | Output Voltage (V) | Power Rating (kVA) | Efficiency (%) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 400 | 230 | 10 | 95 | Marine Equipment |
| Model B | 480 | 240 | 15 | 92 | Submersible Pumps |
| Model C | 600 | 380 | 20 | 90 | Offshore Platforms |
| Model D | 450 | 220 | 12 | 93 | Underwater Stations |
| Model E | 390 | 210 | 8 | 94 | Aquaculture Systems |
| Model F | 480 | 250 | 18 | 89 | Renewable Energy Platforms |
| Model G | 360 | 220 | 9 | 91 | Marine Research Vessels |
| Model H | 420 | 240 | 14 | 92 | Fishing Vessels |
| Model I | 500 | 300 | 25 | 88 | Diving Support Vessels |
| Model J | 450 | 230 | 11 | 90 | Hydrographic Survey Boats |
